Using a ESP8266 Wifi Module
The information on this page refers to firmware v2.30 and higher.
Since firmware version v2.28e, communication via Wifi using the popular ESP8266 Wifi module is supported.
Ordering Information
Things to have at minimum:
- ESP8266 Wifi Module with 1 MB (8 Mb) flash
- USB-to-serial adapter or v3.x STorM32 board
The ESP8266 Wifi module in the list is obvious. If you are using a v1.x STorM32 board, when a USB-to-serial adapter is needed in addition. It is required for flashing the ESP8266 module with a dedicated firmware and upload other files to the ESP8266. However, you probably have one anyhow. For STorM32 v3.x boards a USB-TTL adapter is not needed.
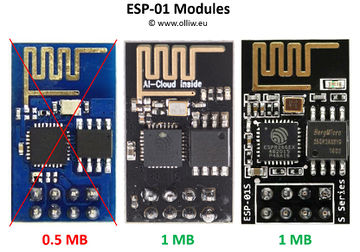
It is important to get the correct ESP8266 module. Quite many different versions are available, see e.g. [1]. You need a module with 1 MB (8 Mb) flash, since the STorM32's ESP firmware is made for that flash size.
In principle, any ESP8266 module with said flash size can be used. For the STorM32 v3.x boards adapter PCBs for hosting a ESP-01 module are available. The original ESP-01 module has only 512 KB (4 Mb) flash and is thus not suitable. You need a "new" ESP-01 module, which nowadays are in fact mostly sold. These are typically black instead of blue, and come with a label "AI-Cloud inside", or as ESP-01s "s series". However, as always with this Asian stuff, one can't be absolutely sure, so buy with care.
Power Supply
The ESP8266 requires 3.3 V, but is quite power hungry and attention needs to be paid to the power scheme. The average power consumption is not critical, the ESP8266 however consumes the power in burst of up to several 100 mA, and the power supply must be able to handle that. Therefore, the ESP8266 module must not be powered from the 3.3 V rail on the STorM32 boards.
The v3.3x STorM32 board provides a ESP8266 port, which exposes the 5 V power rail. The ESP8266 can be powered from this using a 3.3 V voltage regulator with sufficient capacitance. A dedicated ESP8266 adapter board has been designed:
Setup
Before the ESP8266 module can be used with the STorM32, it needs to be flashed with a dedicated firmware, and some data files need to be uploaded. Also, the ESP8266 support needs to be enabled in the GUI. The procedure is different for the v1.x and v3.x STorM32 boards.
v3.x STorM32 Boards
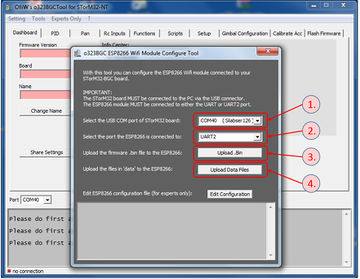
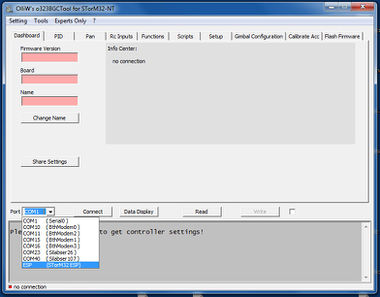
For v3.x STorM32 boards, the configuration of the ESP8266 module can be conveniently achieved by using the [GUI:ESP Configure Tool], which is accessible from the [GUI:Tools] menu in the GUI. Just go through these steps.
- Connect the STorM32 controller via its USB port to a PC. Note: The STorM32 controller must be connected via its USB port, and not via any of the UART ports.
- Select the USB COM port of the STorM32 controller.
- Select the UART port the ESP8266 module is connected to. For v3.x STorM32 boards this would normally be “uart2”. This setting will be written into the parameter Esp Configuration.
- Flash the ESP8266 with the proper firmware by hitting the [GUI:Upload .Bin] button. This brings up a DOS box. Please wait until it has finished, and then press any key to close it.
- Upload the data files to the ESP8266 by hitting the [GUI:Upload Data Files] button. This brings up a DOS box. Please wait until it has finished, and then press any key to close it.
- Repower both the STorM32 and ESP8266 boards. Note: You must repower both, resetting only the STorM32 board is not sufficient.
v1.x STorM32 Boards
In the following steps you will flash the ESP8266 module with the dedicated firmware, upload some data files to the ESP8266 module, connect the ESP8266 module to the STorM32 controller, and configure the ESP support in the GUI.
- Connecting the ESP8266 to the USB-TTL Adapter: For flashing, the USB-TTL adapter needs to be connected to the ESP, the GPIO0 pin connected with Gnd, and the ESP module be reset. These steps are explained in countless posts on the web, so please choose the one of your liking (google).
- Flashing the ESP8266: Bring the ESP module into flash mode as described in step (1). Open a file explorer and browse to the directory 'o323BgcEspWebApp' in your STorM32 firmware folder. Hit cmd-here.bat, which should open a DOS box. Enter 'uploadInoBin.bat COM??' (without quotation marks), where COM?? should be the correct COM port the USB-TTL adapter is assigned to, and hit enter. The flashing should start now.
- Uploading of Data Files to the ESP8266: Bring the ESP module again into flash mode as described in step (1). In the DOS box enter now 'uploadDataToFs.bat COM??' (without quotation marks), where COM?? should be the COM port of the USB-TTL adapter as before, and hit enter. The data upload should start now.
- Connecting the ESP8266 to the STorM32: The ESP module needs to be connected to the UART port on the STorM32 controller.
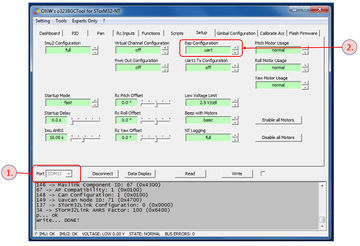
- Configuring the ESP support in the GUI: Connect the STorM32 board via one of the serial ports to your PC, select the correct port in the [Port] field, and hit [Connect] (do not use the Wifi connection, but a standard serial connection). Then browse to the [GUI:Setup] tab, and set the parameter Esp Configuration to “uart”. Write+Store the settings to the board, and repower. You must repower both the STorM32 and ESP boards; resetting only the STorM32 board is not sufficient.
Comment: The ESP module is quite power hungry, it needs up to ca. 250 mA. Do not connect it to the 3.3 V supply on the STorM32 board. Power it by a separate 3.3 V BEC. Do not apply voltages larger than 3.3 V to the ESP module, this will destroy it immediately.
What is the parameter Esp Configuration for?
The ESP8266 Wifi module has the nasty property that it sends out junk on its UART at startup. In order to avoid that this junk data upsets the STorM32 controller, the UART port to which the ESP8266 is connected to needs a special handling. This special handling is enabled by the Esp Configuration parameter.
Enabling the special handling implies that the respective UART port doesn't work normally. For instance, using it to connect to the GUI via a USB-TTL adapter won't work as expected.
It is not strictly mandatory to use the special handling, i.e., setting Esp Configuration to “off” is possible. However, doing so implies to count on ones luck that the ESP8266 startup junk doesn't upset the STorM32 controller.
ESP8266 Operation Modes
The ESP can be run in different operation modes. You can set and configure the mode by corresponding entries in the storm32web.cfg file, which is located in the data file folder, and which you just uploaded together with some other files in that folder. In the following, we will use the default configuration, which is the AP Bridge mode. The ESP provides then an access point, with these credentials:
- SSID = STorM32 ESP
- password = thisisgreat
- url = 192.168.4.1
- port = 80
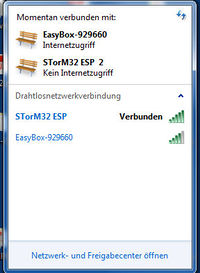
When powered up, you should find an entry 'STorM32 ESP' in the WLAN list. For using it you will of course have to connect to it.
The AP Bridge mode provides Wifi access the STorM32 via both the GUI or the STorM32 Web App, but not both at the same time. Also, once the STorM32 Web App has been called, a connection to the GUI via Wifi is not possible anymore (using first the GUI, and then the STorM32 Web App works fine, but not vice versa). In order to get Wifi access again via the GUI, you have to reset the STorM32 controller (or enter '192.168.4.1/apbridge' in the browser).
Comment: This is so because for connecting with the GUI the ESP is switched internally to work as a bridge while for running the STorM32 Web App the ESP is switched internally to act as a web server. It is possible to switch from bridge to web server operation, but not back.
GUI
Using the Wifi connection with the GUI is trivial. When your WLAN is connected to the access point 'STorM32 ESP', an entry 'ESP (STorM32 ESP)' should show up in the drop down list of the [Port] field. Select it, that's it. All GUI functions should work as normal.
Comment: It may happen that the connection hangs for few seconds at the first connection. This is because Windows has enumerated the access point, which lets the 'ESP (STorM32 ESP)' entry appear in the list, but is not yet really ready, as also indicated by the mouse cursor.
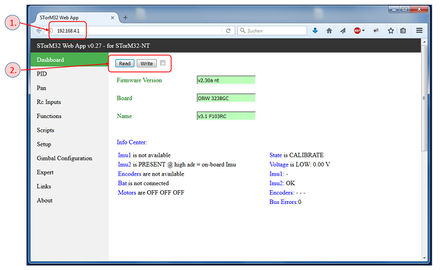
Web Browser: STorM32 Web App
The STorM32 Web App is an attempt to provide platform independent configuration of the STorM32 controller, for mobiles and desktops.
It works as follows: The ESP module runs a web server, at the URL given in the chapter ESP8266 Operation Modes. Thus, with your device (mobile or desktop) you just need to establish a Wifi connection to the ESP module, start a web browser, and browser to the said URL. The ESP isn't very fast, so the loading of the web page takes a couple of seconds.
Currently, the STorM32 Web App provides only very basic configuration possibilities; all parameters can be read, modified and written and stored.
Call for Contributions
I'm not an experienced web page programmer, and I'm especially weak on web design. In short, any contribution in that regard would be most appreciated. You are greatly encouraged to create your own styles, and improve the javascript file.
This is made very easy, I think, by the STorM32's ESP firmware. The modified .js and .css (and even . htm) files just need to be uploaded to the ESP, as described before in the chapter Installation. Even better for development, one can set options in the storm32web.cfg file such that the .js and .css files are fetched from your private web space, which makes the development cycle very fast. See storm32web.cfg for details.